병합 정렬 (Merge Sort)
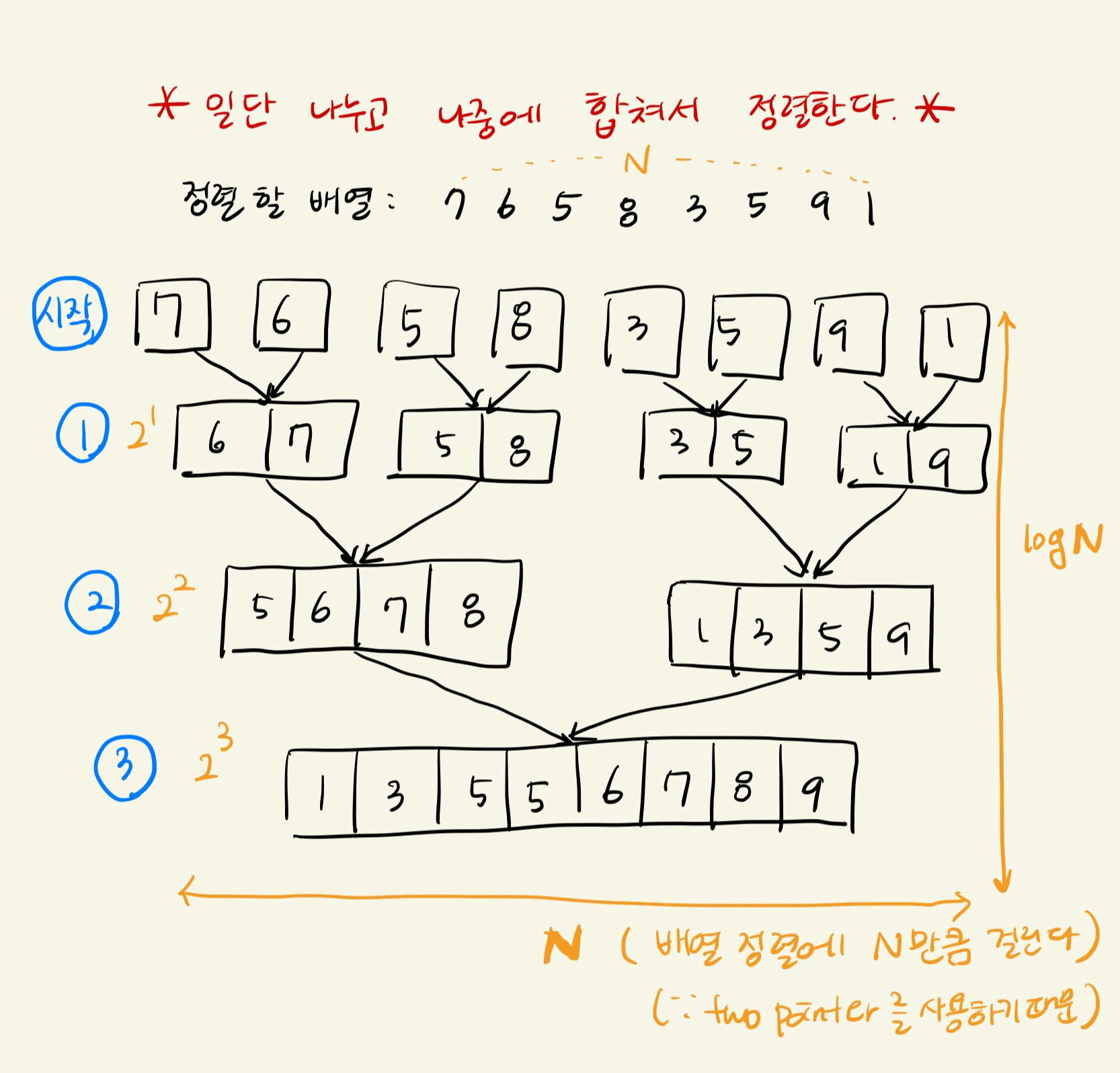
시간 복잡도
항상 O(NlogN)
정렬하는데 필요한 시간은 two pointer알고리즘을 사용하므로 수행시간은 N이다.
합치는 개수는 2배씩 증가하므로 2^3 = 8 로 3단계가 필요하다. 따라서 단계의 크기는 데이터의 갯수가 N개일 때 logN을 유지하게 된다.
따라서 항상 시간복잡도가 O(NlogN)을 유지한다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class p05_mergeSort {
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr) {
sort(arr, 0, arr.length);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (high - low < 2) {
return;
}
// 크기가 1보다 큰 경우
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
sort(arr, 0, mid); // 일단 반으로 나누고 나중에 합쳐서 정렬
sort(arr, mid, high);
merge(arr, low, mid, high);
}
private static void merge(int[] arr, int low, int mid, int high) {
int[] temp = new int[high - low];
int t = 0, l = low, h = mid;
// 작은 순서대로 배열에 삽입
while (l < mid && h < high) {
if (arr[l] < arr[h]) {
temp[t++] = arr[l++];
} else {
temp[t++] = arr[h++];
}
}
// 남은 데이터도 삽입
while (l < mid) {
temp[t++] = arr[l++];
}
while (h < high) {
temp[t++] = arr[h++];
}
// 정렬된 배열을 삽입
for (int i = low; i < high; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i - low];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
mergeSort(arr);
for (int x : arr)
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}장점
- 안정정렬이다.
- 시간복잡도가 항상 O(NlogN)이다.
단점
- 기존의 데이터를 담을 추가적인 배열 공간이 필요하므로 메모리 활용이 비효율적이다.
source
https://blog.naver.com/ndb796/221227934987
7. 병합 정렬(Merge Sort)
지난 시간까지 시간 복잡도 O(N ^ 2)인 선택 정렬, 버블 정렬, 삽입 정렬 알고리즘을 공부했습니...
blog.naver.com
https://www.daleseo.com/sort-merge/
[알고리즘] 병합 정렬 - Merge Sort (Python, Java)
Engineering Blog by Dale Seo
www.daleseo.com
'CS > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 힙 (Heap) (0) | 2023.03.14 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 계수정렬(Counting Sort) (0) | 2023.03.13 |
| [Algorithm] 퀵 정렬 (Quick Sort) (0) | 2023.03.12 |
| [Algorithm] 이분 탐색(Binary Search) (1) | 2023.03.12 |
| [Algorithm] 삽입 정렬(Insert Sort) (0) | 2023.03.12 |